How to TIG Weld?
Oct 09, 2023
Mastering TIG Welding: A Comprehensive Guide
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a welding process admired for its precision and versatility. Whether you're a novice welder or a seasoned professional, mastering TIG welding can open doors to a world of opportunities in various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the art of TIG welding, from its fundamentals to advanced techniques, helping you become a proficient TIG welder.
Advantages of TIG Welding
Before diving into the specifics of TIG welding, let's explore some of its key advantages:
- Precision and Control: TIG welding provides unparalleled precision and control over the welding process. Welders can create precise, high-quality welds with minimal distortion.
-
Versatility: TIG welding can be used on a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and exotic alloys. This versatility makes it indispensable in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and art fabrication.
-
Clean and High-quality Welds: TIG welding produces clean, aesthetically pleasing welds with minimal spatter. This is crucial in applications where the appearance of the weld matters, such as food industry equipment and architectural structures. TIG welding consistently produces high-quality welds with excellent strength and integrity. This reliability is crucial in applications where weld failure is not an option.
Now that we've highlighted the advantages of TIG welding, let's delve into the steps to become proficient in this precise welding technique.
What Is TIG Welding And How Does It Work?
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), also known as TIG welding, is a metal joining process widely used to weld steel, stainless steel, and exotic metals such as aluminum, magnesium, nickel alloys, and more. When you start welding, an electric arc is formed between the non-consumable tungsten electrode and the workpiece. Tungsten has one of the highest melting points of 6,191.6°F, so the heat is directed into the weld joint, while the electrode is not consumed like a Stick electrode.
Depending on the thickness of the metal, TIG welding can be a fusion process. In micro TIG applications, or when welding thin metals with little to no gap, the heat of an arc is enough to fuse pieces together. However, when welding thicker pieces with a bigger gap, you will have to add filler material as TIG rods. Like Stick/Arc, TIG welding is a manual process, meaning you'll have to add the filler metal wire by hand.
Similar to MIG welding, the entire TIG welding process is protected by shielding gas. When heat is applied, both tungsten and weld pool are highly vulnerable to contaminants from the atmosphere. Oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases can easily contaminate the molten metal, leading to various weld defects.

Setting Up for TIG Welding
Before striking an arc, proper setup is crucial for a successful TIG welding process. Here are the key steps to follow:
1. Safety: Always prioritize safety when TIG welding. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including a welding helmet with a clear view of the workpiece, welding gloves, and flame-resistant clothing.
2. Select the Right Equipment: Choose a TIG welding machine that suits your needs. Consider factors such as power output, AC/DC capabilities, and portability. Ensure that the machine is in good working condition and properly grounded. 
Save $90 for MIG-250D: MIG(Aluminum)/MAG/TIG/MMA
3. Prepare the Workpiece: Clean the workpiece thoroughly to remove any contaminants, rust, or grease. Properly fit and secure the pieces to be welded, ensuring they are clean and free of gaps.
4. Gas Selection: Choose the right shielding gas for your application. Typically, argon is used for most TIG welding jobs. Ensure that your gas supply is clean and free of contaminants
5. Set Welding Parameters: Adjust the welding machine's settings, including amperage, voltage, and gas flow rate, to match the requirements of your welding project. Refer to the welding procedure specifications (WPS) if available.
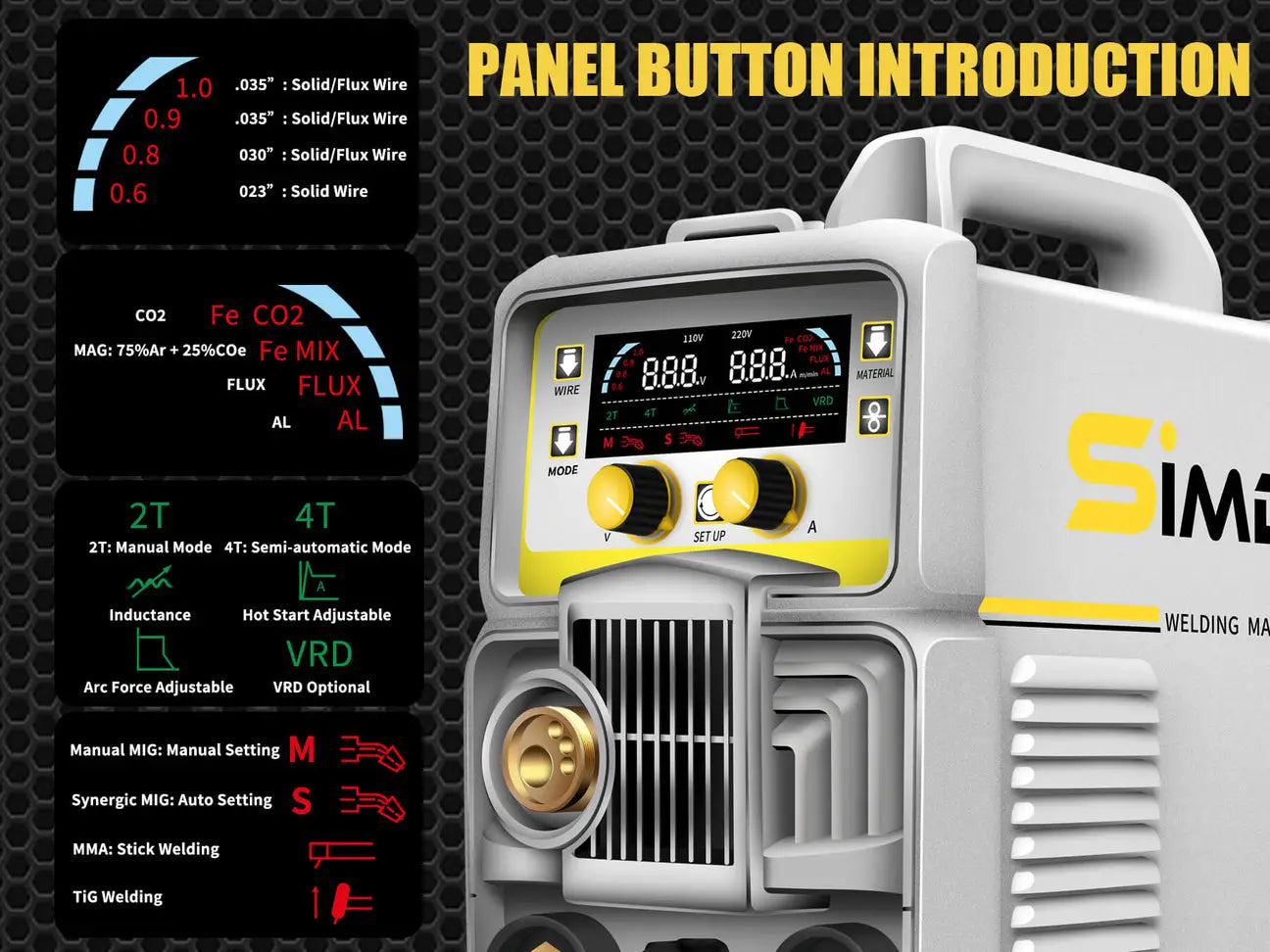
TIG Welding Tips and Best Practices
TIG welding demands precision and finesse. Here are some tips and best practices to improve your TIG welding skills:
- Steady Hand: Maintain a steady hand when guiding the tungsten electrode and filler rod.
- Proper Tungsten Grinding: Sharpen the tungsten electrode correctly to a fine point. A pointed electrode provides better arc stability and control.
- Control the Arc Length: Maintain a consistent arc length between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece. The ideal arc length is typically equal to the diameter of the tungsten electrode.
- Use Proper Angle and Travel Speed: Maintain the correct angle (usually 15-20 degrees) between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece. Control the travel speed to ensure proper fusion and bead shape.
- Clean Welding Surface: Ensure that the welding surface is free of contaminants and oxide layers. Use a stainless steel wire brush to clean the weld area before welding.
With dedication and practice, you can achieve the precision and control that TIG welding is known for. However, it's essential to be aware of common issues that may arise during TIG welding and how to troubleshoot them.
Troubleshooting Common TIG Welding Issues
Even experienced TIG welders encounter challenges from time to time. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Tungsten Contamination: If you notice a blackened or contaminated tungsten electrode, it can affect arc stability. Grind the tungsten to remove contamination, or replace it if necessary.
- Porosity: Porosity in the weld bead can result from inadequate shielding gas coverage or contaminated base material. Ensure proper gas flow and clean workpiece surfaces.
- Incomplete Penetration: If your welds lack penetration, it may be due to insufficient amperage or travel speed. Adjust the settings accordingly to achieve proper penetration.
- Inconsistent Bead Shape: Inconsistent bead shape can result from inconsistent travel speed or improper torch angle. Practice maintaining a steady speed and angle for uniform beads.
- Cracking: Weld cracking may occur due to high heat input or improper joint preparation. Use proper welding techniques and ensure the joint is clean and properly beveled.
By addressing these common issues and continuously honing your TIG welding skills, you can become a proficient TIG welder capable of producing high-quality welds on a variety of materials.
Conclusion
TIG welding is an art that demands precision, patience, and practice. Its ability to create clean, high-quality welds on a variety of materials has made it a favorite among welders in industries ranging from aerospace to automotive. With the right equipment, setup, and techniques, you can master the art of TIG welding and unlock a world of welding opportunities.
So, whether you aspire to weld aircraft components, automotive exhausts, or intricate artwork, TIG welding is a skill worth mastering. With dedication and continuous learning, you can become a proficient TIG welder capable of producing welds of exceptional quality.
Remember, practice makes perfect, and TIG welding is no exception. Happy welding!




